Rajasthan became the first state to legislation the rights of gig workers in India 23 Registration and Welfare Bill, 2023.
The Rajasthan Platform-Based Gig Workers (Registration and Welfare) Bill, 2023.
The Bill applies to aggregators digital intermediaries connecting buyers and sellers, the primary employers individual or organizations platform-based workers.
The Bill proposes a Welfare Board comprising State officials five representatives each from gig workers and aggregators, and two others from civil society. the board will facilitate guarantee of social security to platform-based gig workers.
The Board will maintain a database of companies and workers and each worker will receive a unique ID which shall be valid in perpetuity.
The welfare board will enable gig workers to register with all state aggregators there by ensuring better access to opportunities and benefits. Now in India gig workforce is expected to reach 23.5 million by 2030.
Table of Contents
What is meaning of GIG workers
The Gig workers refer to workers outside of the traditional employer-employee relationship.
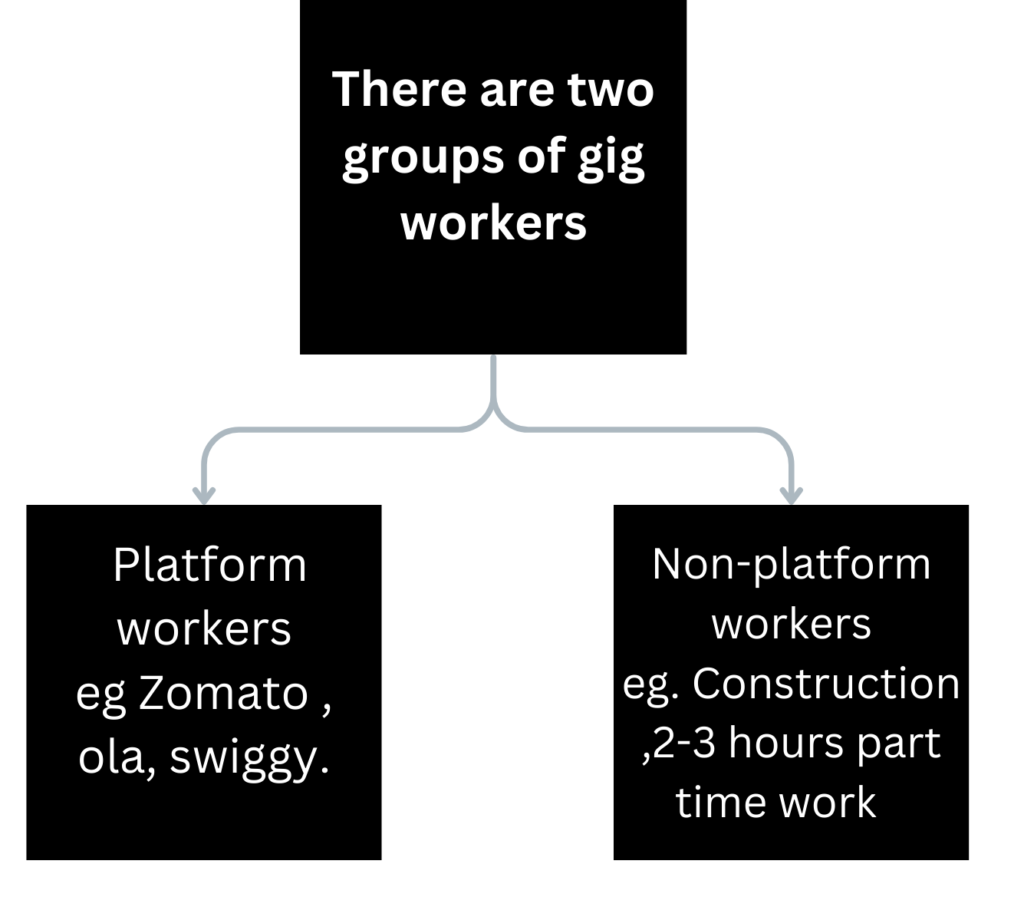
Platform workers
When gig workers use online algorithmic matching platforms or apps to connect with customers, they are called platform workers, eg. Zomato , ola, swiggy.
Non-platform workers
Those who work outside the above platforms are non-platform workers, including construction workers and non-technology-based temporary workers, eg. Construction ,2-3 hours part time work
Half a the billion labour force, India has already emerged as one of the world largest countries of gig workforce due to pandemic and rising factors access to internet, digital technology and smartphones in India.
What is role of GIG economy in india
The gig workforce is expected to expand to 2.35 crore (23.5 million) workers by 2029–30.
According to a report India’s Booming Gig and Platform Economy released by NITI Aayog , 77 lakh workers were engaged in the gig economy in 2020–21. They constituted 2.6% of the non-agricultural workforce or 1.5% of the total workforce in India.
Gig workers are expected to form 6.7% of the non-agricultural workforce or 4.1% of the total livelihood in India by 2029–30. At present, about 47% of the gig work is in medium skilled jobs, about 22% in high skilled, and about 31% in low skilled jobs. Trend shows the concentration of workers in medium skills is gradually declining and that of the low skilled and high skilled is increasing.
Technology
The rise of technology, which has made it easier for people to find and work with clients online.
Work Flexibility
The increasing demand for flexible work arrangements, which allows people to balance work and other commitments.
Demographic Factors
The growing number of young people in India, who are more likely to be open to working in the gig economy.
RECOMMENDATIONS BY NITI AAYOG
A Platform India initiative, built on the pillars of accelerating platform by simplification and handholding, funding support and incentives, skill development, and social financial inclusion, like the immensely successful Startup India initiative, may be introduced.
Access to Skill and Finance
Provide financial products and cash flow-based loans to platform workers. Platforms can collaborate with the Ministry of Skill Development to promote skilling and job creation in the gig economy.
Focus on Women
It recommends businesses to implement programs for workers and their families that raise knowledge of gender issues and accessibility, especially to advance the rights of women and people with disabilities.
Data Collection
Other recommendations include undertaking a separate enumeration exercise to estimate the size of the gig and platform workforce and collecting information during official enumerations Periodic Labour Force Survey to identify gig workers.
Free trade agreement
creating pathways for education and certification acquired in India to be recognised globally, such as through FTAs.
Innovation
Platforms and businesses can innovate to create new models that provide gig workers with better pay, benefits, and job security. This could include the development of new technologies, such as block-chain and AI that enable more transparent and secure gig work arrangements.
Advantages gig workers
1. Gig workers have the flexibility to work according to their own schedule and availability, and can often choose their own work hours.
2. Companies can save costs by hiring gig workers instead of full-time employees, and may be able to provide services more economically to users.
3. The gig economy provides jobs for many low and semi-skilled workers, often with minimal conditions.
4. Gig workers can save costs by working remotely and avoiding expenses like office commute Low Power.
5. Entrepreneurial Opportunities Gig work can also offer entrepreneurial opportunities, allowing workers to start their own businesses or work as independent contractors with multiple clients.
6. Income Generation: Gig work can provide a source of income for individuals who may not have access to traditional employment, such as those with disabilities or those living in remote areas.
7. Gig work may be isolating, as gig workers often work independently and may not have the same social connections or support networks as traditional employees.
Disadvantages of gig workers
1. Job Insecurity often the work on a day-to-day basis and may be terminated without notice, as seen during the pandemic.
2. Gig workers typically have no social security benefits, paid leave, or wage regulation, and may be at the mercy of platform companies
3. Poor Work Conditions many gig workers are required to work long hours with little transparency on incentive structures and may have little bargaining power.
4. Unequal Treatment may time subject to unfair treatment or exploitation such as low pay, long working hours, or unsafe working conditions.
5. Limited Career Growth not have access to training or development programs, or be able to build long-term relationships with clients.
6. Social Isolation as gig workers often work independently and may not have the same social connections or support networks as traditional employees
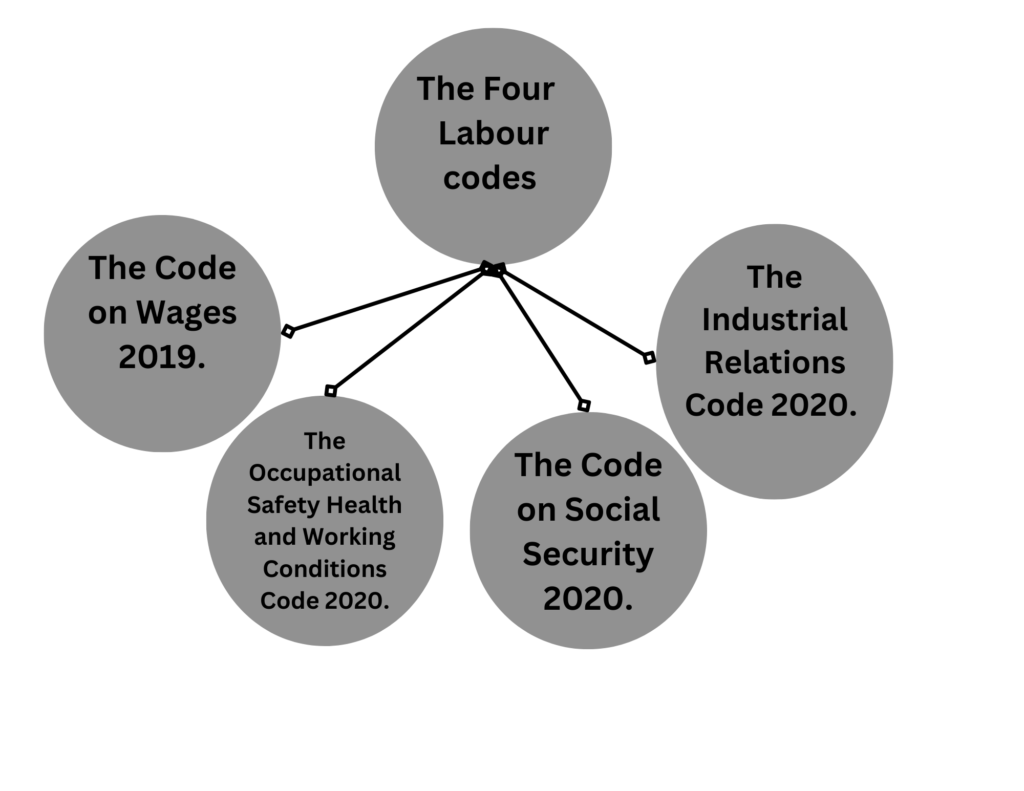
The new Labour codes
The overcome to gig work problems to under the low the new labour codes seek to consolidate 29 existing statutes on labour that require a critical reformation since decades. implement the process states are to finalize their rules under these codes. The codes are based on recommendations of the Second National Commission on Labour (2002)
What are the benefits this code
Out of the four new labour codes proposed, gig work finds reference only in the Code on Social Security. As a result, gig workers remain excluded from vital benefits and protections offered by other Codes such as minimum wage, occupational safety etc.
Moreover, they remain excluded from accessing the specialized redressal mechanism under the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947, denying them an effective remedy for grievances against their employers.
Considering the non-traditional nature of their work, gig workers also do not have the right to collective bargaining — a fundamental principle of modern labour law crucial to safeguard the rights of workers
New Code on social security 2020
The unique nature of gig work, gig workers display characteristics of both employees and independent contractors and thus do not squarely fit into any rigid categorization.gig workers have limited recognition under current employment laws and thus fall outside the ambit of statutory benefits. CODE ON SOCIAL SECURITY, 2020.
The Ministry of Labour and Employment introduced the Code on Social Security, 2020 which brings gig workers within the ambit of labour laws for the first time.
Definition of gig worker as per the code 2020
Under section 2(35) of the Code, a ‘gig worker’ is defined as a person who performs work or participates in a work arrangement and earns from such activities outside of a traditional employer-employee relationship.
The Code defines platform work as a work arrangement outside of a traditional employeremployee relationship in which organisations or individuals use an online platform to access other or individuals to solve specific problems or to provide specific services in exchange for payment.
The Code stipulates that Central and State governments must frame suitable social security schemes for gig workers on matters relating to health and maternity benefits, provident funds and accident benefits among others. The Code also mandates the compulsory registration of all gig workers and platform workers to avail of the benefits under these schemes.
E-Sharm portal
To create database of unorganized workers including gig workers it is created to give social security benefits for Eg. Entitlement to get accidental insurance benefits under Pradhan mantra suraksha bima yojana [PMSBY]
if you read about AI future in India click the link
Conclusion
If we talking about gig workers in India lot of access to internet and digital technology day by day grow with employer – employee online plat-form to created new job for youth. The bill and code implement by government in India.
QA
Can gig workers is safe in India
Yes, gig worker is safe Indian code 2020,online platform to access other or individuals to solve specific problems or to provide specific services in exchange for payment.
Government any schemes for gig workers
Yes government E-Sharm portal to gig workers accidental insurance benefit to social security.



[…] if you read for gig worker click the link […]